In the era of emerging technologies, data has become essential for organizations. With rapid digital transformation across industries, gaining a competitive advantage is crucial for thriving in the market. Today, data is the new “oil” that forms an organization’s core for business growth. However, the rate of data generation has become enormous. A recent report by Towards Data Science produced the statistics of data generation that stands at a whopping 2.5 quintillion bytes. Additionally, the current projections state the data generation rate to rise to 133 zettabytes by 2025.
In recent years, the increase in the number of data breach cases has doubled. The imminent threat in a business is the possibility of data breaches. To bolster data protection, it is of utmost importance to have a robust data governance framework. As per IBM data breach reports, the average cost of a data breach is highlighted as $3.86 million, while the USA alone recorded a breach of $8.64 million.
There is a need for robust data governance framework to tackle such challenges. Standard data governance ensures data security, data quality, and integrity while providing the traceability of the data origins. Also, data governance can be successfully implemented when high-quality data is readily available with crucial information on the data types, which is achievable with a data catalog. Besides, an organization attains firm control over its data usage policies when a regulatory body imposes stricter guidelines. Today, it is possible with some of the robust regulatory bodies available that put a strong emphasis on data governance. Among them, the most well-known is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Furthermore, a data governance approach can reach its ultimate goal within an enterprise with its essential components, namely processes, policies, access controls, and data protection, encompassing the entire data-related workflow within an organization. Tech giants such as Microsoft have contributed significantly to the data governance requirements with the Azure Purview offering that has reach achieved wide acceptance in the industry.
The article delves into the topic to provide a deep insight into data governance and its regulations.
Data Governance Overview
Data governance is a strategy that incorporates the practices, processes, and technical requirements of an organization into a framework by which an organization can achieve standardization in its workflow, thereby providing protection and the appropriate management of its data assets. A useful data governance model’s scalability is a must as it ensures that all the policies, processes, and use-cases are applied accurately for transforming a business into a data-driven enterprise.
Another crucial aspect of data governance is for an organization to conduct a risk assessment and compliance. The successful integration of data governance is determined by efficient data management and data security factors within the framework. An ideal governance policy must address the critical components of data storage, the original source, and a well-defined data access strategy. Furthermore, data governance solutions focus on providing response plans relating to misuse of data and unauthorized access.
Data governance and data management are often used synonymously, but it is essential to understand that data governance forms a significant part of a data management model.
Data Catalog
A data catalog acts as the inventory of the critical data assets in an organization. The use of metadata helps to manage the data more efficiently. The data professionals benefit from a data catalog as it helps in data collection, organizing data, easier accessibility to data, and improvement of the metadata to support data discovery and governance. While the data generated is enormous in a day to day functioning of an organization, finding relevant data becomes challenging for specific tasks. Additionally, data accessibility is demanding due to various legal regulations of the organization and a particular country’s government. The key factors to understand are the data movement within an organization, such as the individuals who will have access to it and the purpose they want to access it. Such tracking of the data ensures the protection of the data as it limits unauthorized personnel. Thus a data catalog plays a crucial role in addressing some of the challenges related to data.
- A data catalog provides all the essential data required by an organization; therefore, data accessibility from a single point ensures reduced time for searching data.
- Creating a business vocabulary.
- Efficient transformation of data lakes into data swamps.
- Identifying the different structures of the data.
- Availability of high-quality and reliable data.
- Data reusability possibilities
An organization can achieve a competitive advantage with the appropriate use of data. Therefore the data should be trustworthy from the appropriate sources. Some of the organizations’ key members, such as C-level executives, use data for business decisions. Thus, a data catalog becomes useful for looking at cost-saving and operational efficiency factors with a keen eye on fraud and risk analysis.
Data Governance Framework
A data governance framework allows an organization to focus on achieving the business goals and data management challenges while providing the right means to attain them more speedily and securely. Besides, the results of a data governance integration are scalable and measurable.
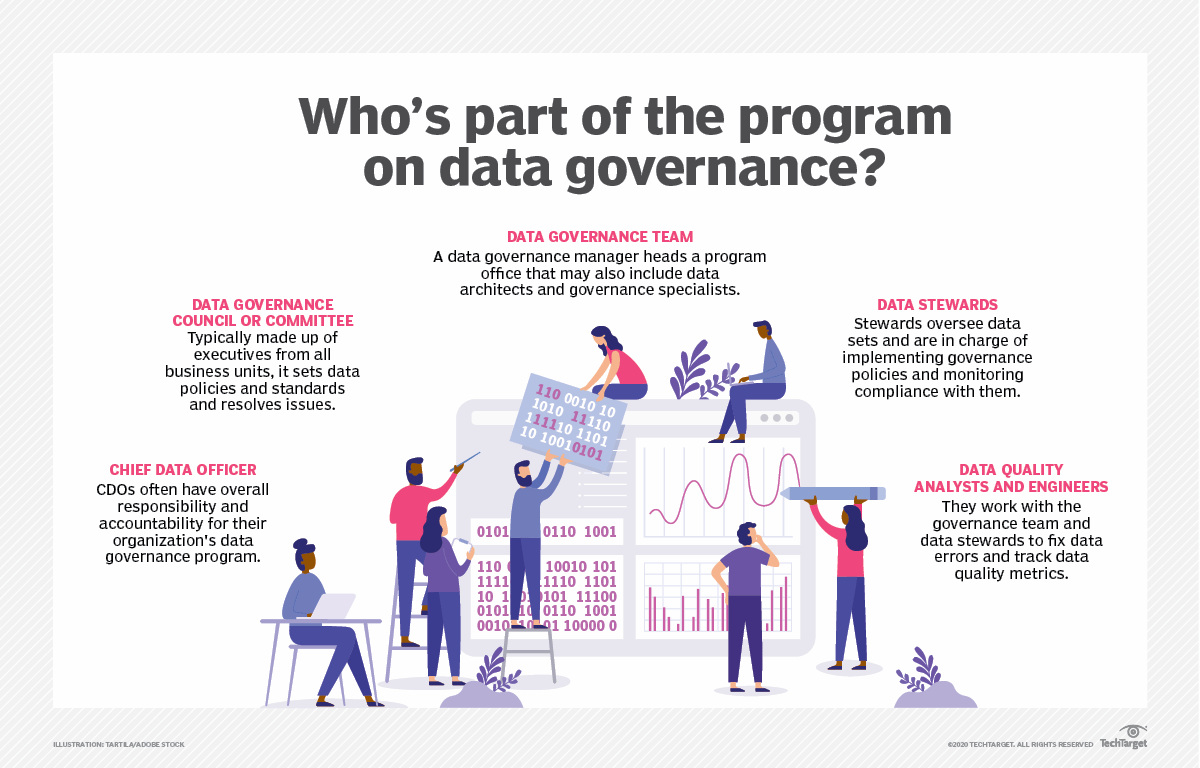
Figure. Key Participants in a Data Governance Framework. Source
Some of the essentials of a data governance framework are:
- Use Cases
The data governance framework must address some critical factors, such as the use case for several business scenarios in an organization. The data governance use cases should interlink the need for a data governance framework and its contribution to achieving business goals. Ideally, the use cases are derived from significant factors in an organization, such as revenue, cost, and the associated risks. The category-related use case addresses the enrichment of products and services, innovations, market opportunities, and the ability to achieve them at a reduced cost of maintenance with efficiency, auditing, and data protection.
- Quantification
The need to quantify data is an absolute necessity as it produces data governance integration in the organization. A business needs to ascertain that they are following, covering all the categorized use cases with evidence to monitor the performance and provide future insights.
- Technical Benefits
With the technical addition in a workflow, the data governance solutions can efficiently address some of the critical components, thereby ensuring efficiency. The data governance must address factors like the need for technology investment and the primary members who will work with data-related processes. A technical infusion in the workflow also enables the easier discoverability of data definitions, data categories, data lineage, and the appropriate classification of data as trustable data or untrustworthy data. The technical addition also makes it possible to create a feedback mechanism for resolving regulatory issues and policies concerning data usage.
- Scalability
The data governance policies should be capable of providing scalable results. Using a scalable model provides growth opportunities for an organization by addressing the problems in a data lifecycle. The primary focus is to introduce new tools to reduce operational costs and provide data protection for business growth.
Data Governance Processes
The data government processes comprise of the following.
- The organization must be mindful of the essential documents such as regulatory guidelines, statutes, company policies, and strategies.
- A clearly defined workflow states legal mandates, policies, and objectives to be synchronized to help an organization meet data governance and management compliance.
- Data metrics to be incorporated to measure the performance and the quality of the data.
- Principles of data governance to be met.
- Identification of the data security and privacy threats.
- Control measures to ensure smoother data flow with a precise analysis of the risks.
Data Governance Policies
Under data governance, there are various policies to determine the effectiveness of the organization’s operational strategies. Some of the policies related to data accessibility, data usage, and data integrity are incredibly crucial for successful data governance implementation. The most important policies that an organization must follow for successful data management are as follows.
- Data Structure policy
- Data Access Policy
- Data Usage Policy
- Data Integration Policy
Privacy and Compliance Requisites
The organizations are associated with a significant amount of highly sensitive data. Therefore, an organization needs to follow the regulatory compliance of data governance. In the context of business, privacy refers to an individuals’ right to have control over the type of personal data they want to be collected and used and the sensitive information that should be restricted. As per EU directives for data governance, sensitive data is defined as the data that contains a name, address, telephone number, and email address of an individual. On the other hand, sensitive personal data is distinguished clearly, as the data contains information on a person’s ethnicity, political opinion, religion, race, health-based information, criminal conviction, and trade union-based membership details. Such data have stricter guidelines that must be followed with due diligence.
Role of General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) was established in the year 2016. The primary aim of the regulation was to provide a framework for data privacy standards. GDPR states that any company looking to conduct business in Europe must be willing to adhere to data protection norms. The GDPR has strict guidelines that ensure the protection and privacy of personal data for its citizens. The mandate was an update from the previous Data Protection Directive in Europe.
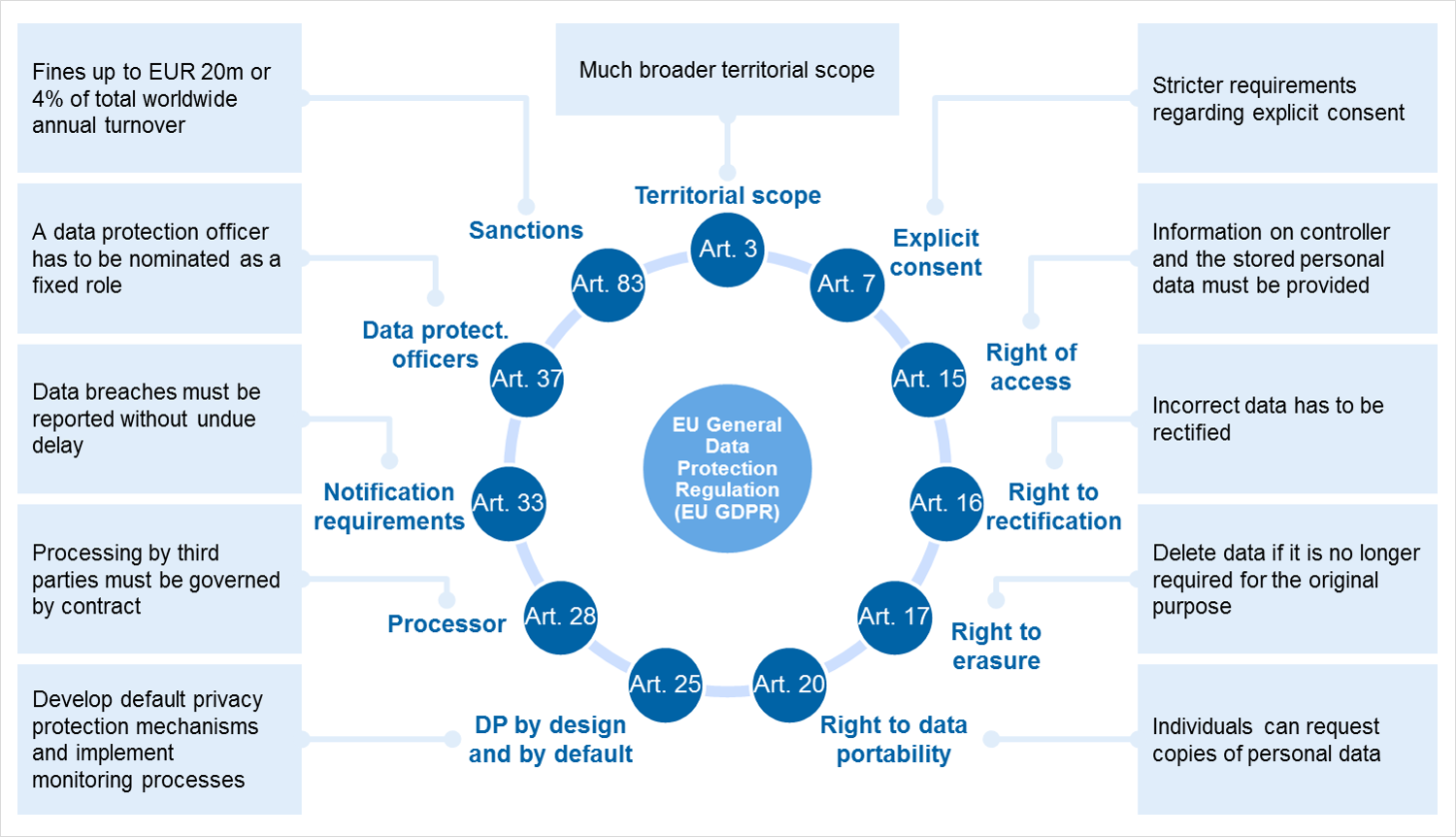
Figure. Crucial Requirements of GDPR. Source
Under GDPR, the mandate’s scope extends its reach in terms of the territorial horizon while providing a well-defined law for processing personal data by offering their business services in Europe. The organizations or individuals aiming to provide their services without the presence in Europe are monitored for their service offering under GDPR guidelines. The tracking of such services includes online businesses that require users to accept cookies to access their services. GDPR also differentiates the various data types and the data considered personal data under the mandate.
Furthermore, the direct and indirect data are interlinked with the identification of data subjects. The data subjects are people who can be identified with their information presented in the data. The data in this context is related to personal information such as names, addresses, IP addresses, biometric data logs, citizenship-based identification, email, and the profession.
Additionally, the GPPR mandate ensures that the data is collected within the limits of the law, and it should be highly secured while it exists the records of the organization with stricter rules for its uses. The primary categories of GDPR data governance requirements are:
- There must be a classification of personal data, while personal identification data must have limited usability. The individuals can access their data and hold the right to request personal data removal or rectification. The mandate also states mandatory data processing requirements and portability of data.
- Data protection is a must, and it should cover all aspects of safeguarding personal data collected. Also, there must be confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the data collected for business purposes. The organizations should also adhere to data restoration regulations for scenarios that may involve data loss due to technical failure or accidents.
- The collected data must be well- documented as per legal procedures.
Access Controls
Access controls form an integral part of access governance that regulates the accessibility of data. The critical areas covered comprise the guidelines to specify who can access the data and view it. Additionally, it specifies that there is a requirement to state the purpose of data access in the organization. The compliance of access controls allows eliminating unauthorized access of data.
As per the GDPR mandate, some of the data protection requirements must enforce specific procedures.
- There must be accountability associated with data protection requirements. Data protection personnel must be appointed to manage data and monitor its activities for organizations involved in data processing activities. The appointed individuals must ensure that the data protection standards are met.
- Data storage is the essential factor for data privacy. Therefore, organizations must have a data map and data inventory to track the source of data and its storage. The source includes the system from which it was generated while tracking the data lineage to provide comprehensive data protection.
- Data accuracy is paramount, and organizations must keep up-to-date data to achieve high-quality data. Also, data quality reporting must be followed to keep up with data quality standards.
Data Protection
- Data intelligence provisions for getting insights with 360 visibility of data.
- Identifying data remedies for security and privacy issues.
- To protect sensitive data with access governance and ensure no overexposed data exists with data governance methods.
- Integrating artificial intelligence capabilities to identify dark data and its relationship.
- Assigning labels with automation to provide data protection during the workflow and the lifecycle of the data.
- Rapid data breach notification and its investigation.
- Automate procedure for classifying sensitive and personal data.
- Automated compliance and policy checks.
- In-depth assessment of risk scores with metrics depending on the data type, location, and access consent.
Reimagining Data Governance with Microsoft Azure Purview
Azure Purview is a unified data governance service by Microsoft. The governance service enables management and governing of on-premise, multi-cloud, and software-as-a-service (SaaS) data. The users can have access to a holistic and up-to-date map of the data with automated data discovery. Besides, the classification of sensitive data is more manageable along with end-to-end data lineage. With Azure Purview, the data consumers are assured of valuable and trustworthy data. Some of the key features of Azure Purview are discussed in the following section.
- Unified mapping of data
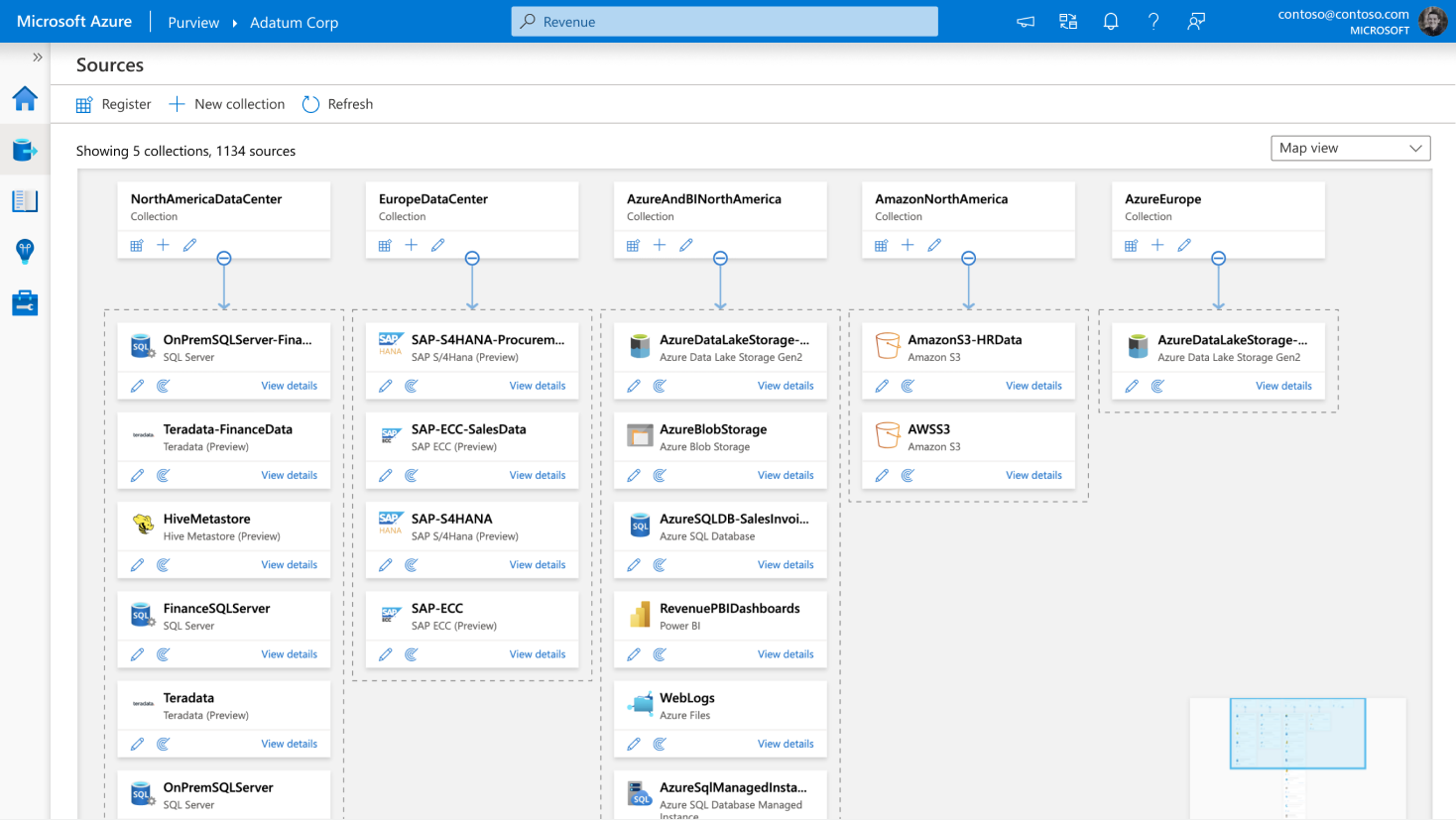
The Purview data map feature establishes the foundation of practical data usage while following the data governance standards. With Purview, it is possible to automate the management of metadata from hybrid sources. The consumer can take advantage of data classification with built-in classifiers that can Microsoft Protection sensitivity labels. Finally, all the data can be easily integrated using Apache Atlas API.
Figure. Unified Data Mapping using Azure Purview. Source
- Trusted Data
Purview offers a data catalog feature that can allow the easier search of data using technical terms from the data vocabulary. The data can be easily identified as per the sensitivity level of the data.
- Business Insights
The data supply chain can be interpreted conveniently from raw data to gain business insights. Purview offers the option to scan the power BI environment and the analytical workspace automatically. Besides, all the assets can be discovered with their lineage to the Purview data map.
- Maximizing Business Value
The SQL server data is more discoverable with a unified data governance service. It is possible to connect the SQL server with a Purview data map to achieve automated scanning and data classification.
- Purview Data Catalog
The Purview data catalog provides importing the existing data dictionaries, providing a business-grade glossary of terms that makes data discoverable more efficiently.
Conclusion
Business enterprises are generating a staggering amount of data daily. The appropriate use of data can be an asset for gaining business value in an organization. Therefore, organizations need to obtain reliable data that can provide meaningful business insights. Advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and data analytics provide an effective way of integrating data governance in the operational workflow. Today, tech giants like Microsoft, with their data governance offering: Azure Purview, have paved the way for other organizations to opt for data governance. Many startups follow in the footsteps and have acknowledged the importance of data governance for high-quality data while ensuring data privacy at all times, thereby offering several data governance solutions in the market. A robust data governance framework is essential for maintaining the data integrity of the business and its customers.